Brushing, Flossing, and Rinsing: The Trio for a Healthy, Bright Smile
Achieving and maintaining a healthy smile requires a consistent and thorough oral hygiene routine. Brushing, flossing, and rinsing are the three essential steps that work together to keep your teeth and gums in top shape. Each step has its unique benefits. When combined, they provide comprehensive care that prevents cavities, fights gum disease, and keeps your breath fresh. Here’s how each part of this trio contributes to your dental health and why it’s important to make all three a daily habit.
Brushing: The Foundation of Oral Health
 Brushing twice daily is the foundation of a healthy smile. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, brush for two full minutes in the morning and before bed. Brushing removes plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, that builds up on your teeth and can lead to cavities and gum disease if left unchecked. Make sure to brush along the gumline and on all surfaces of each tooth—front, back, and chewing surfaces.
Brushing twice daily is the foundation of a healthy smile. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, brush for two full minutes in the morning and before bed. Brushing removes plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, that builds up on your teeth and can lead to cavities and gum disease if left unchecked. Make sure to brush along the gumline and on all surfaces of each tooth—front, back, and chewing surfaces.
Use gentle, circular motions rather than harsh, back-and-forth scrubbing to avoid irritating your gums and wearing down enamel. Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles start to fray, to ensure effective cleaning. Proper brushing keeps plaque levels low, supports strong enamel, and promotes healthy gums.
Flossing: Reaching Between the Teeth
While brushing cleans the visible surfaces of your teeth, flossing reaches the tight spaces between teeth where food particles and plaque love to hide. Skipping flossing allows bacteria to accumulate in these areas, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease. By flossing daily, you remove debris that brushing alone can’t reach, preventing plaque buildup and keeping your gums healthy.
To floss effectively, use about 18 inches of floss and gently slide it between each pair of teeth, curving it around the base of each tooth and moving it up and down. If traditional flossing is difficult, consider using floss picks or a water flosser to make the process more convenient. Flossing is crucial for a complete clean and plays a major role in gum health, which ultimately supports overall dental health.
Rinsing: The Final Step for Freshness and Protection
Rinsing with an antiseptic or fluoride mouthwash is the final step in a complete oral care routine. It helps flush out remaining bacteria and particles, reaching areas that brushing and flossing might have missed. Look for a mouthwash with antibacterial properties to reduce harmful bacteria, freshen your breath, and, if it contains fluoride, strengthen enamel to prevent decay.
Rinse for about 30 seconds, swishing the mouthwash around all areas of your mouth. Avoid eating or drinking immediately afterward to allow the ingredients to work. Rinsing also helps maintain fresh breath, especially when combined with brushing and flossing.
The Power of Consistency
Brushing, flossing, and rinsing together create a powerful defense against cavities, gum disease, and bad breath. By committing to this trio every day, you protect your smile, maintain fresh breath, and avoid costly dental issues down the road. A few minutes each day spent on brushing, flossing, and rinsing makes a lasting difference, giving you the confidence of a healthy, bright smile. Embrace this trio, and enjoy the lifelong benefits of a strong, vibrant smile.


 Key Ingredients to Consider
Key Ingredients to Consider
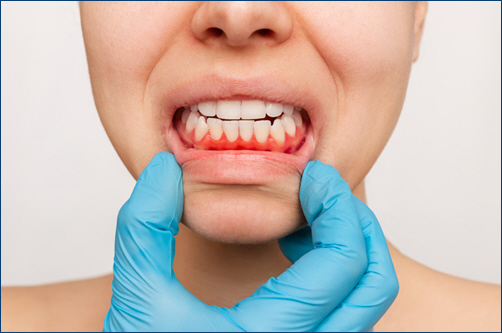 Regular Dental Checkups
Regular Dental Checkups
 The connection between oral health and heart health is primarily due to the role of inflammation and bacteria. The mouth is a gateway to the body, and poor oral hygiene can lead to the buildup of bacteria and plaque. If not addressed, this can result in gum disease (periodontal disease), which is characterized by inflammation of the gums and the structures supporting the teeth.
The connection between oral health and heart health is primarily due to the role of inflammation and bacteria. The mouth is a gateway to the body, and poor oral hygiene can lead to the buildup of bacteria and plaque. If not addressed, this can result in gum disease (periodontal disease), which is characterized by inflammation of the gums and the structures supporting the teeth.